Update: Gold (XAU / USD) reported a risk level, up 0.26% overnight near $ 1,832, to hit its first six-day high on Wednesday. Market sentiment appears to have led to more early warnings about commodity prices (CPI). In addition, geopolitical challenges in the Middle East and vaccine reforms exacerbated by the price of gold could affect the search for human bulls.
While risk catalysts and market meetings are profitable when the European conference can directly stimulate asset movement, gold traders will want to learn more about the softer US. The CPI for April was assumed to be 3.6% compared to 2.6% previously.
At the time of writing, XAU / USD was flat in Asia after a mixed day and night. The price rose to $ 1,836 after a day of uncertainty and a strong improvement with the daily line-up gave the bulls an attractive price.
The rapid decline in Asian commodities was thought to have happened earlier this week when Europeans went online, which also got wet on Wall Street.
US gains with G10 and gold have fared better during a weak period.
On the eve of the US consumer price index, traders predicted that an increase in inflation would push the dollar and US dollar to a 2-1 / 2-month low at the beginning of New York.
The dollar strengthened around levels on Tuesday afternoon.
The industry generally believes the Federal Reserve will pursue lower interest rates and greater investment, which is a long-term boost for good steel.
In the US economy, financial concerns about the recession have pushed up commodity prices.
The return on 2-year government money increased by 1 principle from 0.15% to 0.16% and the return on 10-year government money increased by 3 principles by 1.60% for 1.63%.
In the context of key data, the industry expects CPI to rise 0.2% in April, "which will rise to 3.6% year-on-year as a result of fundamentals," the report said. The analyst explains. Westpac explains.
Elsewhere, April's finances were inadequate but rising, and we'll also hear from Federal Reserve Secretary Clarida, who will discuss oversight of the US economy.
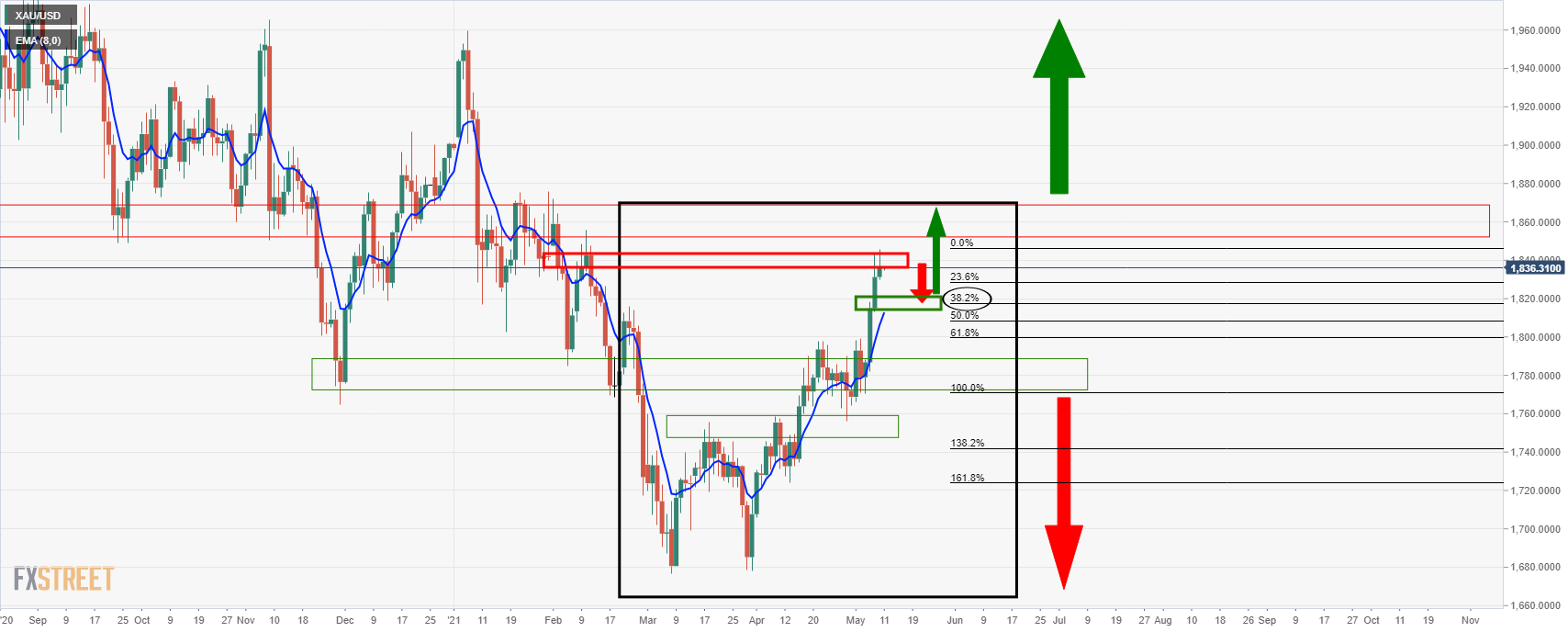
Identification by gold
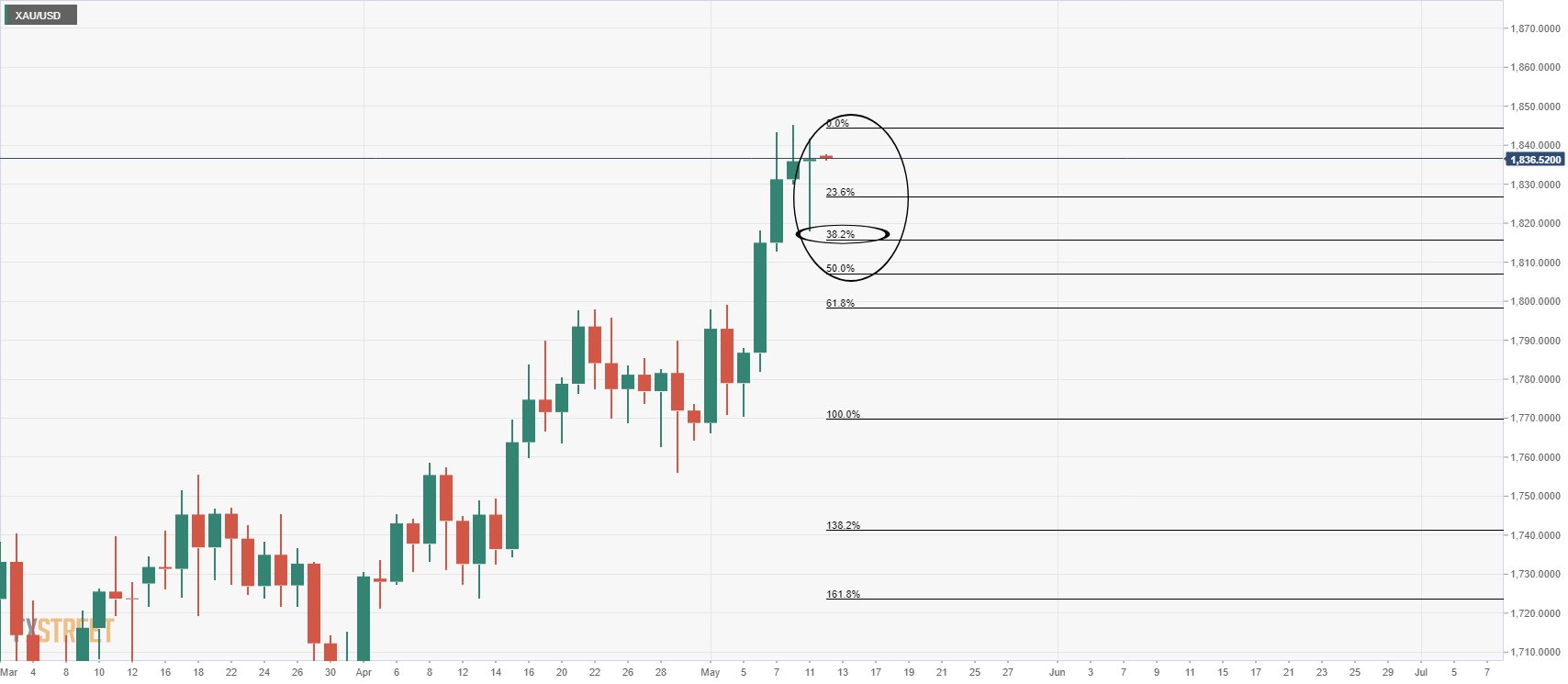
Meanwhile, according to the previous analysis, the correct price is at 38.2% Fibonacci level as below:
As mentioned, the current bullish branch is slightly overloaded and the daily chart is an example of this.
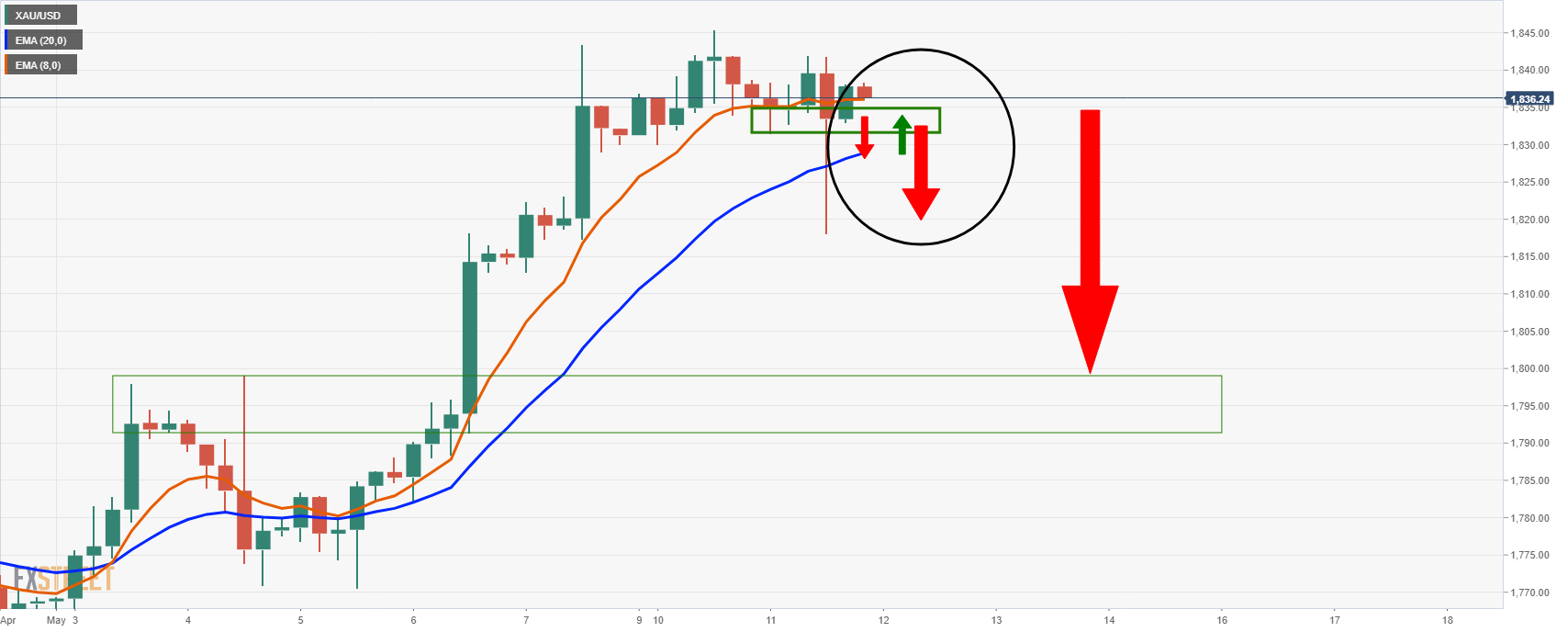
An adjustment of at least 38.2% Fibo that matches the model in the lower timeframe, such as the 4-hour chart, will join 8 EMAs.
If the bulls end up in there, it increases the risk to the supermarket once a month, with 1,850 first ports of call.
The price remains in a strong margin within a 4-hour period, so further inflation will stay here.
That said, if the support breaks, the bearish 8 and 20 EMA will cross the continuation of the remaining support, which is expected to follow the resistance, upset the balance, in line with the Bear.
The bear will focus on the Fibonacci retracement of 61.8% of the daily heart rate corresponding to the early and 1,800 brainstorms.
US Consumer Price Index April Preview:
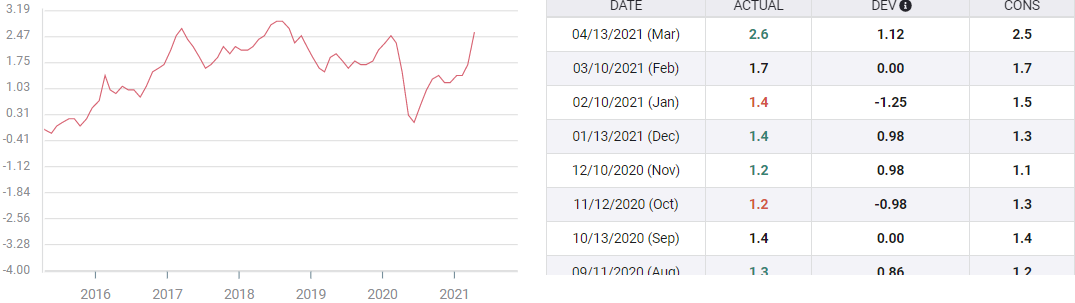
Annual CPI expectations are expected to rise 3.6% in April.
April 2020 saw the lowest number of consumers of communicable diseases.
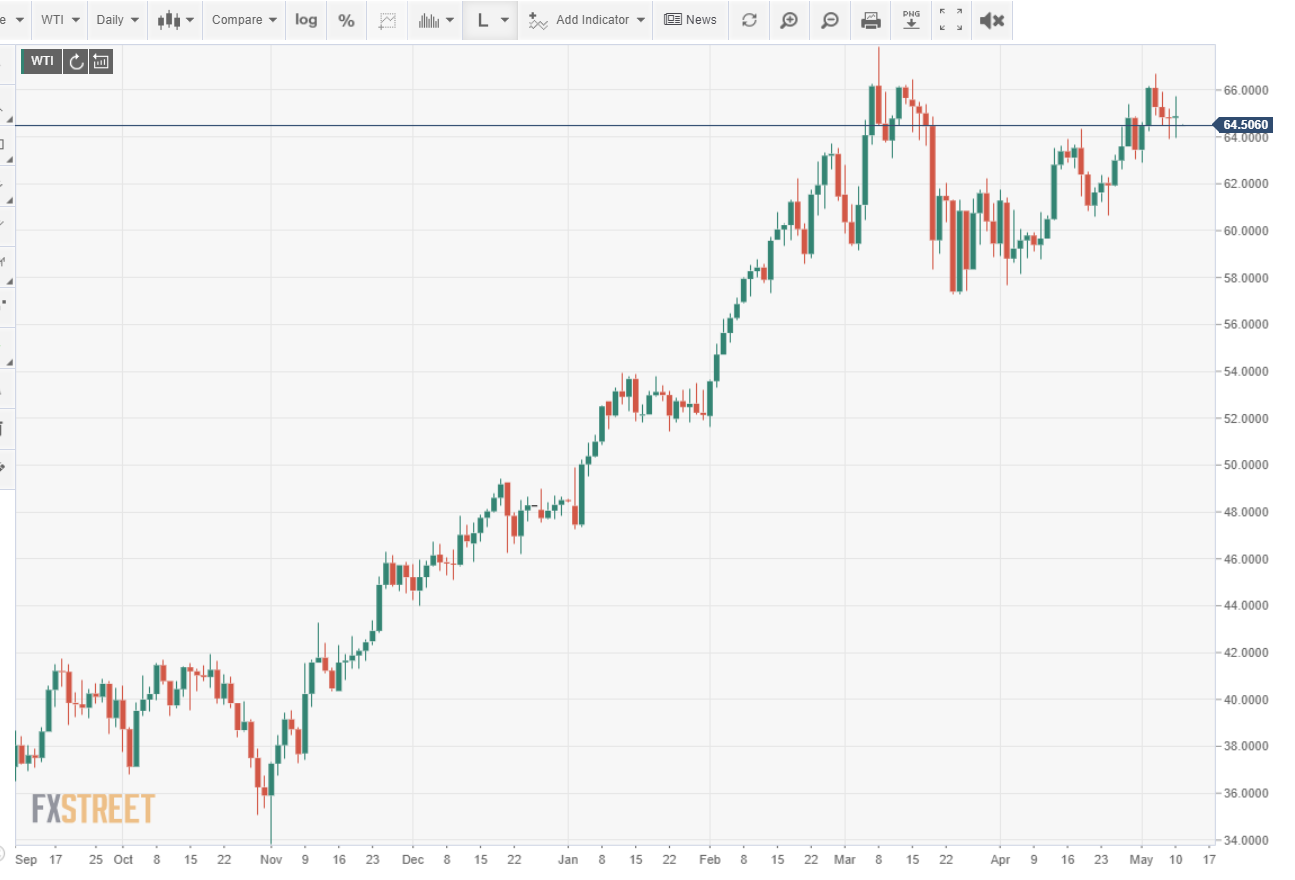
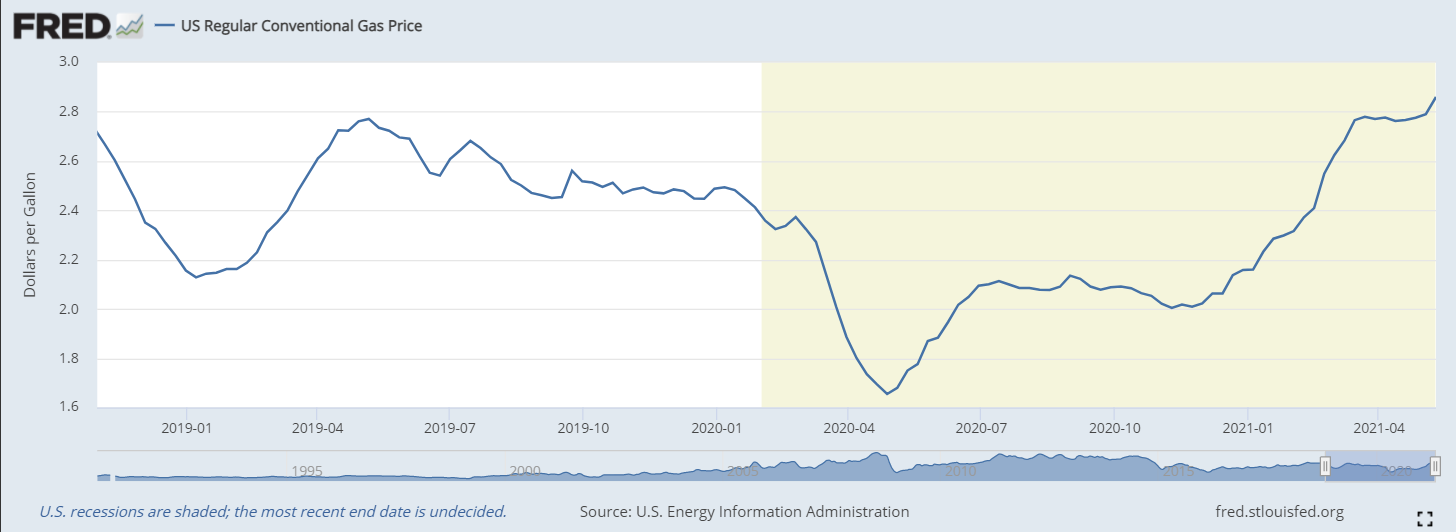
U.S. oil prices rose 43 percent in the month.
The Federal Government does not see any change in policy with inflation.
The U.S. consumer market is expected to peak in the last decade as the base of the spread reaches its peak last year.
The consumer price index (CPI) is expected to rise 0.2% in April, according to a report by Reuters analysts. In March, CPI rose 0.6%. Annual rates are expected to rise by 3.6% after gaining 2.6% in March.
The student rate is expected to remain unchanged at 0.3% per month, but increase 2.3% year-on-year in April from 1.6% in March.
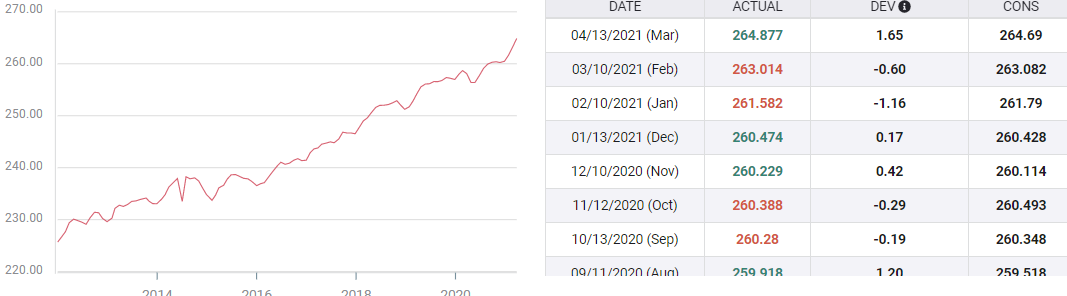
Customer price
The consumer number measures the change in the value of the basket of goods for a period with a year of use equal to 100.
Last year, March and April closed retailers forcing them to sell products at a discount or not at all, as consumers often restricted their purchases for essential products and services. .
When it closed last spring, the index fell from 258,678 in February to 258,115 in March to a low of 256,389 in April 2020.
Customer price
Prices started well in May, and at the July 259,101 score, the index was higher than the February benchmark assessment.
Since July last year, inflation has risen by an average of 0.3% per month. In March, gains were up from the index at 264,877, or 2.62% higher than the March 258.115.
A similar comparison with the April 2020 measure is expected to increase by 3.3% this year.
The initial operation of the consumer increases with the short of demand
The fast-paced U.S. economy and more government regulation have boosted consumption. Retail sales rose 4.8% in the first quarter, which, only in May, June and July, reversed after declining, was the strongest in sales. bi-monthly.
The recovery has exposed a wide range of uncertainties in products and services due to horizontal shocks, and fears of over-supply and over-the-counter products. Prices for some products have risen and are likely to rise further when the market is fully open and life resumes.
In addition, electricity prices, which are responsible for almost every consumer, have risen since the last November presidential election.
A group of West Texas Intermediate (WTI), the North American benchmark price is up 79.7% since it opened the day before the Nov. 2 election to $ 35.90.
FXStreet
Oil prices have risen at the same time. From a national average of $ 2.02 higher on Nov. 2, prices rose 43% to $ 2.86 as of May 10. The gains were a combination of the two. demand increased in line with global transmission and the Biden government's policy on electricity, which eliminated all new oil production. lease in federal land.
Government policy to reduce the budget
The Federal Reserve expects a further increase in CPI this year as governors adopt the Federal Reserve in September. Once the financial recovery has begun, the jump in CPI is a fact of mathematics, as long as it is a normal rate.
This new standard allows inflation to pass the target for sufficient time and time constraints to establish an average rate of 2%.
With this change, the Fed lost its response. In the past, financial growth of more than 2% for more than a month or two would have allowed the lending industry to predict higher interest rates.
The purpose of this new information has given the central bank more freedom to control payments regardless of exchange rates.
Conclusion
Fed President Jerome Powell and other officials have repeatedly said that the current wave of inflation is a constraint, largely due to last year’s economic downturn. In that they are true. March and April CPI jumps are changing again.






0 Comments